研究領域腫瘤 細胞生物 免疫學
抗體來源Rabbit
克隆類型Polyclonal
交叉反應Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Dog, Cow, Rabbit, Sheep,
產品應用WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
分 子 量130kDa
細胞定位細胞外基質 分泌型蛋白
性 狀Liquid
濃 度1mg/ml
免 疫 原KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Collagen I:1051-1150/1464
亞 型IgG
純化方法affinity purified by Protein A
儲 存 液0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存條件Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
PubMedPubMed
產品介紹Collagens are highly conserved throughout evolution and are characterised by an uninterrupted "Glycine X Y" triplet repeat that is a necessary part of the triple helical structure. Type I collagen (95 kDa) is found in bone, cornea, skin and tendon. Mutations in the encoding gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta, Ehlers Danlos syndrome, and idiopathic osteoporosis. Reciprocal translocations between chromosomes 17 and 22, where this gene and the gene for Platelet-derived growth factor beta are located, are associated with a particular type of skin tumor called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, resulting from unregulated expression of the growth factor.
Function:
Type I collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen).
Subunit:
Trimers of one alpha 2(I) and two alpha 1(I) chains. Interacts with MRC2. Interacts with TRAM2. Subcellular Location : Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
Subcellular Location:
Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
Tissue Specificity:
Forms the fibrils of tendon, ligaments and bones. In bones the fibrils are mineralized with calcium hydroxyapatite.
Post-translational modifications:
Proline residues at the third position of the tripeptide repeating unit (G-X-P) are hydroxylated in some or all of the chains. Proline residues at the second position of the tripeptide repeating unit (G-P-X) are hydroxylated in some of the chains.
O-linked glycan consists of a Glc-Gal disaccharide bound to the oxygen atom of a post-translationally added hydroxyl group.
DISEASE:
Defects in COL1A1 are the cause of Caffey disease (CAFFD) [MIM:114000]; also known as infantile cortical hyperostosis. Caffey disease is characterized by an infantile episode of massive subperiosteal new bone formation that typically involves the diaphyses of the long bones, mandible, and clavicles. The involved bones may also appear inflamed, with painful swelling and systemic fever often accompanying the illness. The bone changes usually begin before 5 months of age and resolve before 2 years of age.
Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type 1 (EDS1) [MIM:130000]; also known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome gravis. EDS is a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDS1 is the severe form of classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Defects in COL1A1 are the cause of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type 7A (EDS7A) [MIM:130060]; also known as autosomal dominant Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. EDS is a connective tissue disorder characterized by hyperextensible skin, atrophic cutaneous scars due to tissue fragility and joint hyperlaxity. EDS7A is marked by bilateral congenital hip dislocation, hyperlaxity of the joints, and recurrent partial dislocations.
Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 (OI1) [MIM:166200]. A dominantly inherited connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility and blue sclerae. Osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 is non-deforming with normal height or mild short stature, and no dentinogenesis imperfecta.
Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 2 (OI2) [MIM:166210]; also known as osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. A connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility, with many perinatal fractures, severe bowing of long bones, undermineralization, and death in the perinatal period due to respiratory insufficiency.
Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 3 (OI3) [MIM:259420]. A connective tissue disorder characterized by progressively deforming bones, very short stature, a triangular face, severe scoliosis, grayish sclera, and dentinogenesis imperfecta.
Defects in COL1A1 are a cause of osteogenesis imperfecta type 4 (OI4) [MIM:166220]; also known as osteogenesis imperfecta with normal sclerae. A connective tissue disorder characterized by moderately short stature, mild to moderate scoliosis, grayish or white sclera and dentinogenesis imperfecta.
Genetic variations in COL1A1 are a cause of susceptibility to osteoporosis (OSTEOP) [MIM:166710]; also known as involutional or senile osteoporosis or postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is characterized by reduced bone mass, disruption of bone microarchitecture without alteration in the composition of bone. Osteoporotic bones are more at risk of fracture.
Note=A chromosomal aberration involving COL1A1 is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGF.
Similarity:
Belongs to the fibrillar collagen family.
Contains 1 fibrillar collagen NC1 domain.
Contains 1 VWFC domain.
SWISS:
P02452
Gene ID:
1277
Database links:
Entrez Gene: 1277 Human
· Entrez Gene: 12842 Mouse
· Entrez Gene: 100008952 Rabbit
· Entrez Gene: 29393 Rat
· Omim: 120150 Human
· SwissProt: P02453 Cow
· SwissProt: O46392 Dog
· SwissProt: P02452 Human
· SwissProt: P11087 Mouse
· SwissProt: P02454 Rat
· Unigene: 172928 Human
· Unigene: 277735 Mouse
· Unigene: 107239 Rat
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications
| 產品圖片 | Sample:
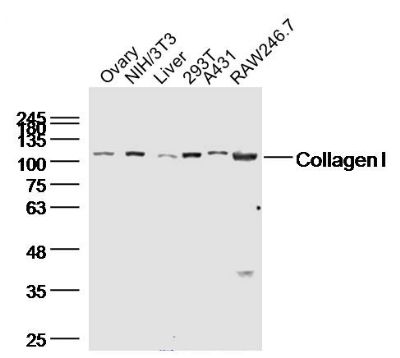
Ovary (Mouse) Lysate at 40 ug
NIH/3T3(huamn) Cell Lysate at 40 ug
Liver (Rat)Lysate at 40 ug
293T(huamn) Cell Lysate at 40 ug
A431(huamn) Cell Lysate at 40 ug
RAW264.7(huamn) Cell Lysate at 40 ug
Primary: Anti-Collagen I (bs-10423R) at 1/300 dilution
Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution
Predicted band size: 95 kD
Observed band size: 110 kD Sample:
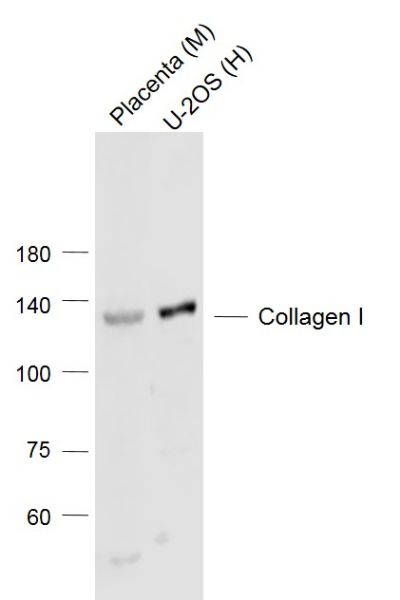
Lane 1: Placenta (Mouse) Lysate at 40 ug
Lane 2: U-2OS (Human) Cell Lysate at 30 ug
Primary: Anti-Collagen I (bs-10423R) at 1/1000 dilution
Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution
Predicted band size: 130’110 kD
Observed band size: 130 kD Sample:
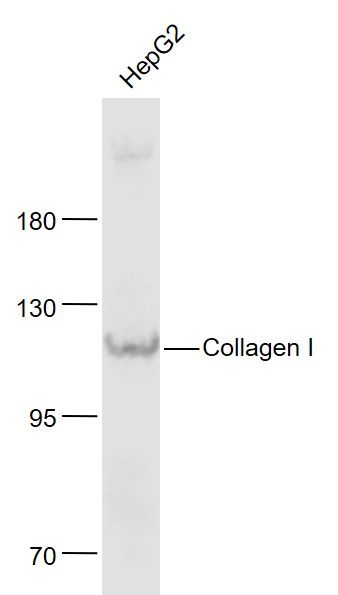
HepG2(Human) Cell Lysate at 30 ug
Primary: Anti- Collagen I (bs-10423R) at 1/1000 dilution
Secondary: IRDye800CW Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG at 1/20000 dilution
Predicted band size: 130 kD
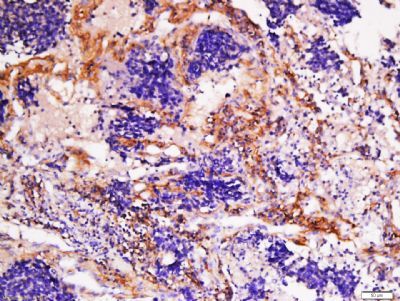
Observed band size: 110 kD Tissue/cell: human lung carcinoma; 4% Paraformaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded;
Antigen retrieval: citrate buffer ( 0.01M, pH 6.0 ), Boiling bathing for 15min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% Hydrogen peroxide for 30min; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum,C-0005) at 37℃ for 20 min;
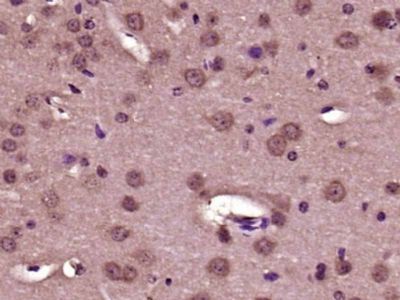
Incubation: Anti-Collagen I Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated(bs-10423R) 1:200, overnight at 4°C, followed by conjugation to the secondary antibody(SP-0023) and DAB(C-0010) staining Paraformaldehyde-fixed, paraffin embedded (Mouse brain); Antigen retrieval by boiling in sodium citrate buffer (pH6.0) for 15min; Block endogenous peroxidase by 3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes; Blocking buffer (normal goat serum) at 37°C for 30min; Antibody incubation with (Collagen I) Polyclonal Antibody, Unconjugated (bs-10423R) at 1:400 overnight at 4°C, followed by operating according to SP Kit(Rabbit) (sp-0023) instructionsand DAB staining. |